Git internal architecture 🏛

Git is a really simple and elegant solution to a complex problem. I think it’s important that we understand what’s going on behind the scenes and the engineering decisions made to fully grasp it’s simplicity and power.
How does Git store files? What happens when we run the various Git commands? How is everything linked? What is the data structure used?
We are going to answer all of the questions below 👇
Initialising the repo
When you run git init in a directory, Git creates the .git directory, which is where almost everything that Git stores and manipulates is located.
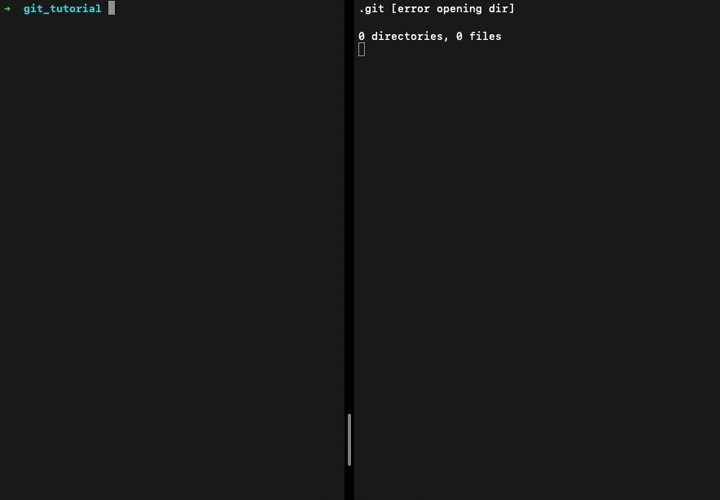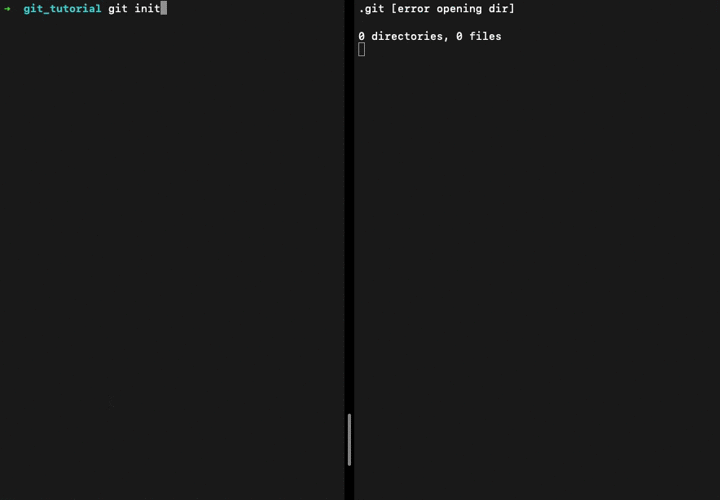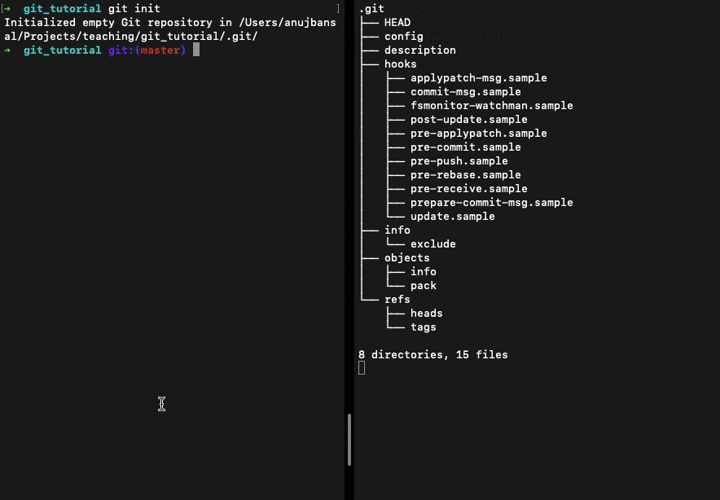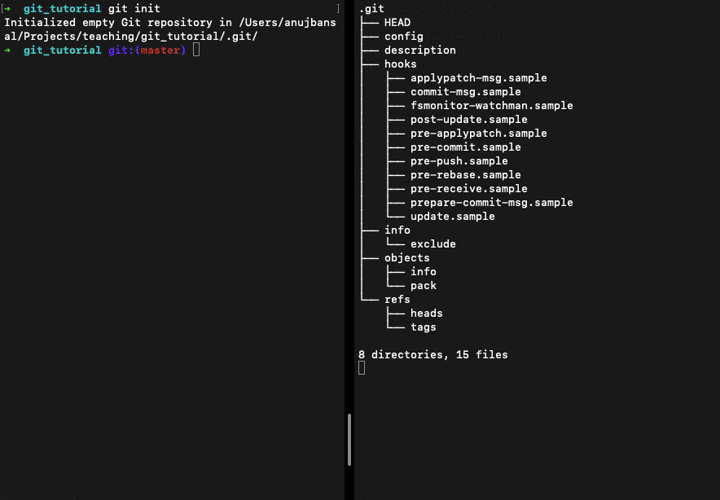
👆 Output of tree .git when we run the git init command
It contains a few different types of files and directories:
- Configuration: the
.git/config,.git/descriptionand.git/info/excludefiles essentially help configure the local repository. - Hooks: the
.git/hooksdirectory contains scripts that can be run on certain lifecycle events of the repository. - Staging Area: the
.git/indexfile (which is not yet present in our tree listing above) will provide a staging area for our working directory. - Object Database: the
.git/objectsdirectory is the default Git object database, which contains all content or pointers to local content. - References: the
.git/refsdirectory is the default location for storing reference pointers for both local and remote branches, tags and heads. A reference is a pointer to an object, usually of typetagorcommit. References are managed outside of the Object Database to allow the references to change where they point to as the repository evolves. Special cases of references may point to other references, e.g.HEAD.
Staging a file
When we run the command git add . Git adds all the changes from the working directory to the staging area and creates blob files in the .git/objects sub-directory.
Each objects file has a 40-char SHA-1 hash as its filename. Git uses the first 2 chars to organise the objects in directories.
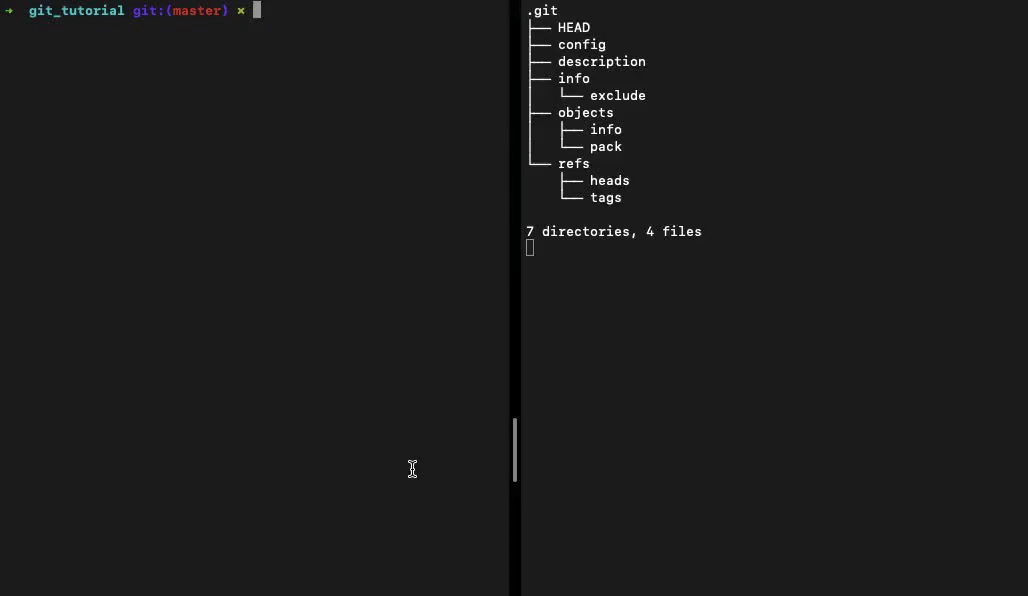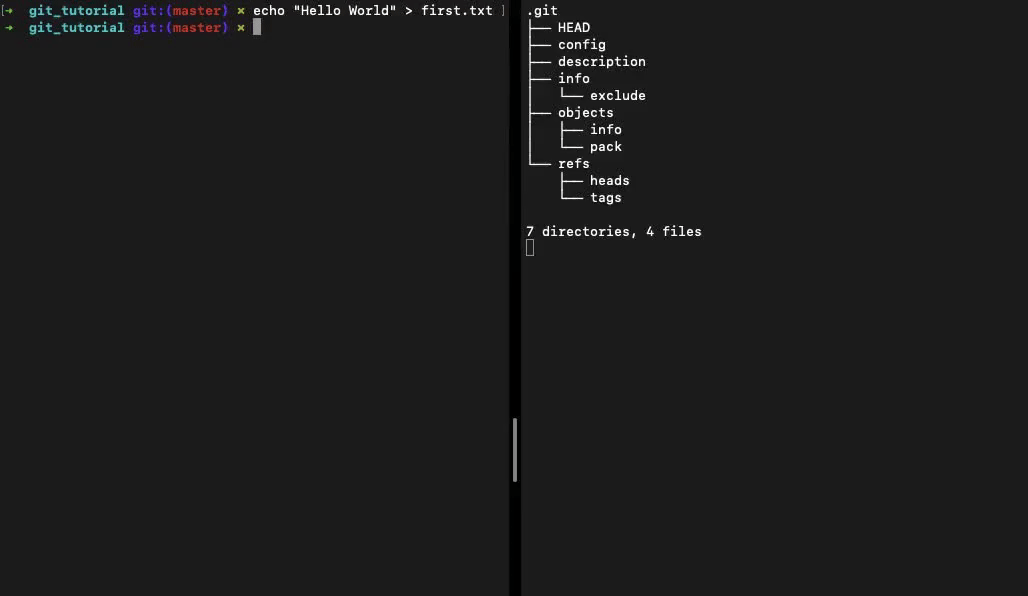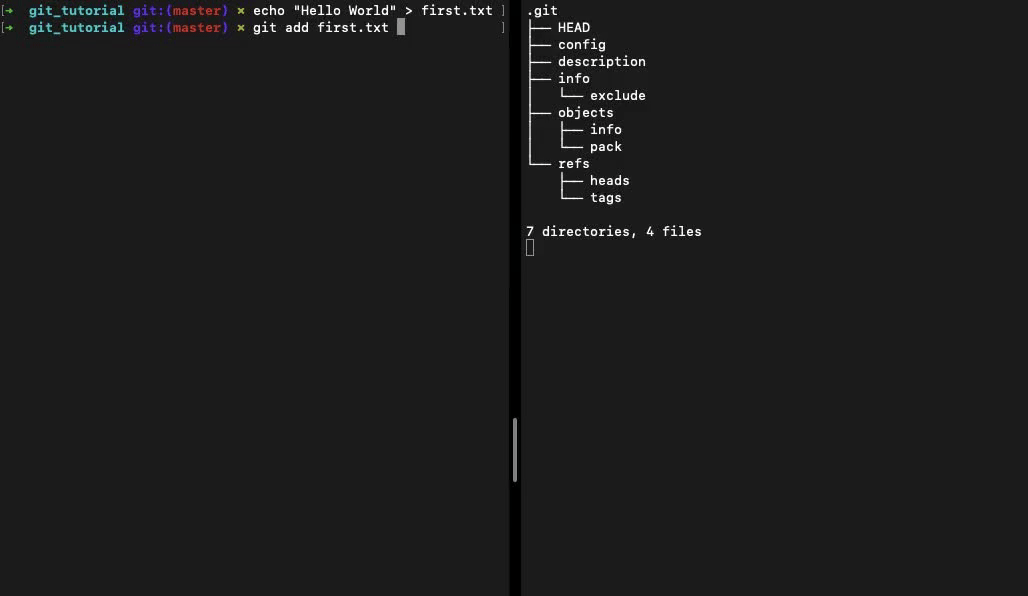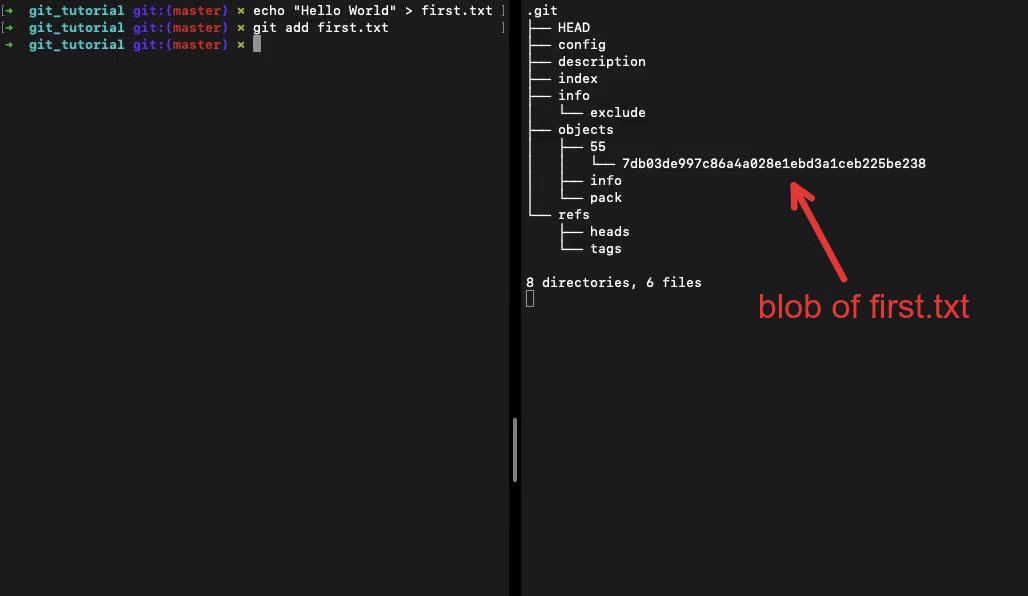
This blob object has the contents of the file. All objects are immutable once created. Making changes to a file and staging it will result in an entirely new object getting created.
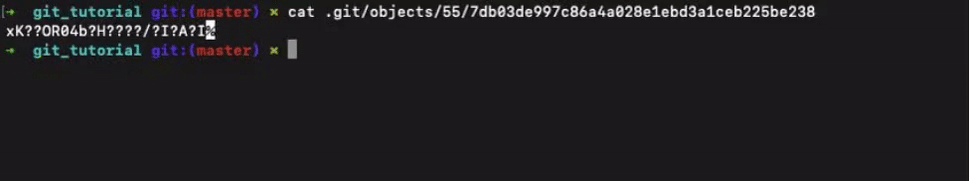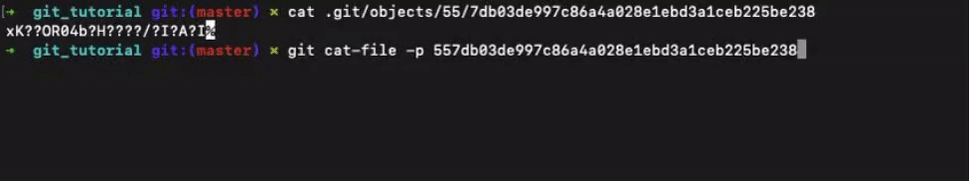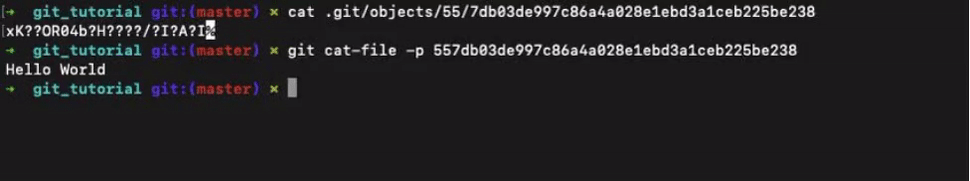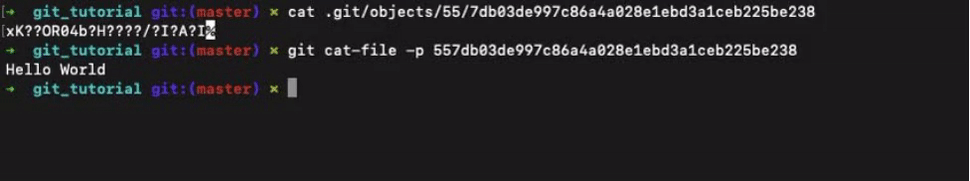
Let’s verify and check the contents of this blob file. When we run the command cat .git/objects/55/7db03de997c86a4a028e1ebd3a1ceb225be238 we don’t get what we expected.
Well, Git actually compresses each and every object using zlib and therefore what you see is the compressed content.
To see the actual file content use the command git cat-file -p <SHA-1>
Commits
Running the git commit command creates two more objects in the objects sub-directory. One is a tree object and the other is a commit object.
Tree Objects
A single tree object contains one or more entries, each of which is the SHA-1 hash of a blob or subtree with its associated mode, type, and filename.
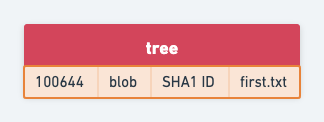
Commit Objects
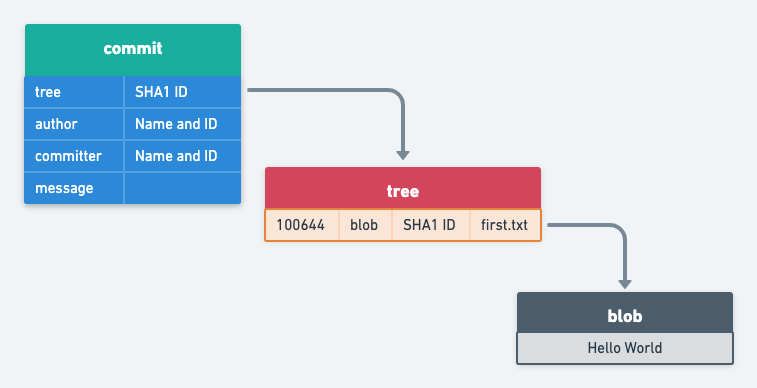
The format for a commit object is simple: it specifies the top-level tree for the snapshot of the project at that point, the parent commits if any, the author/committer information and a commit message.

The commit id that we commonly use is the SHA-1 hash of the contents of the commit object.
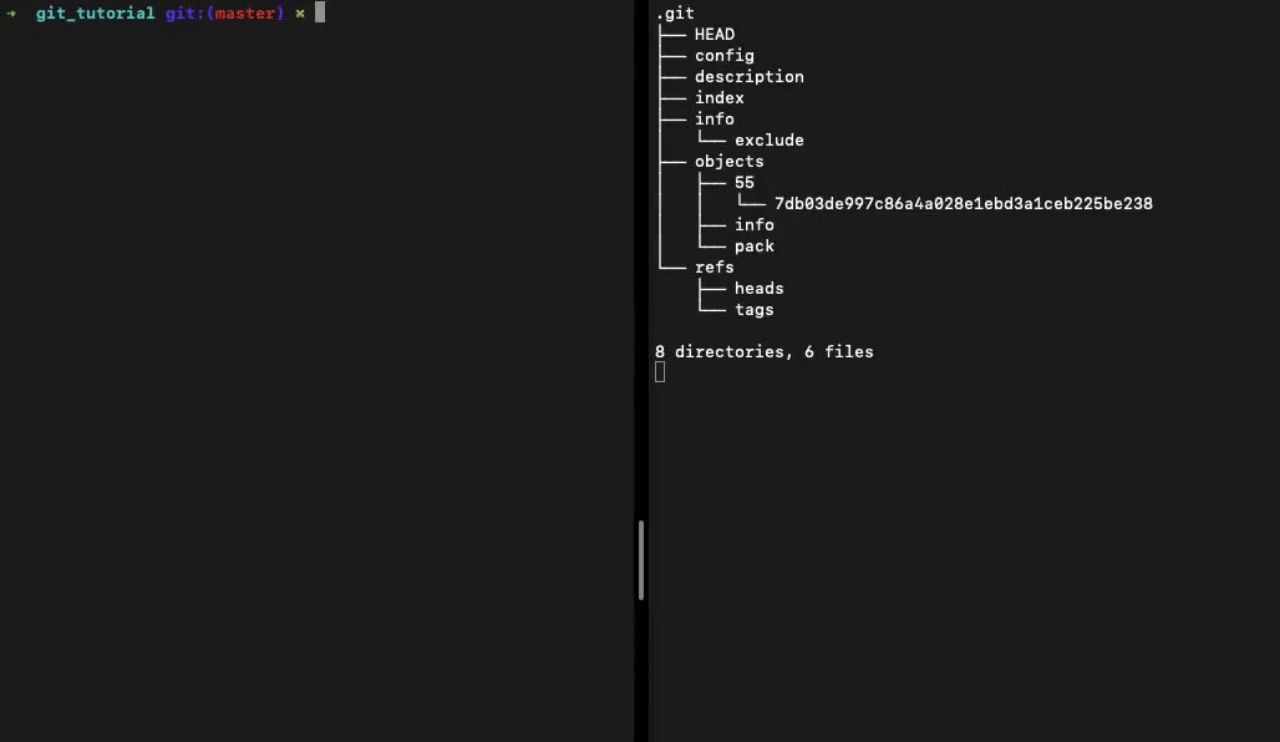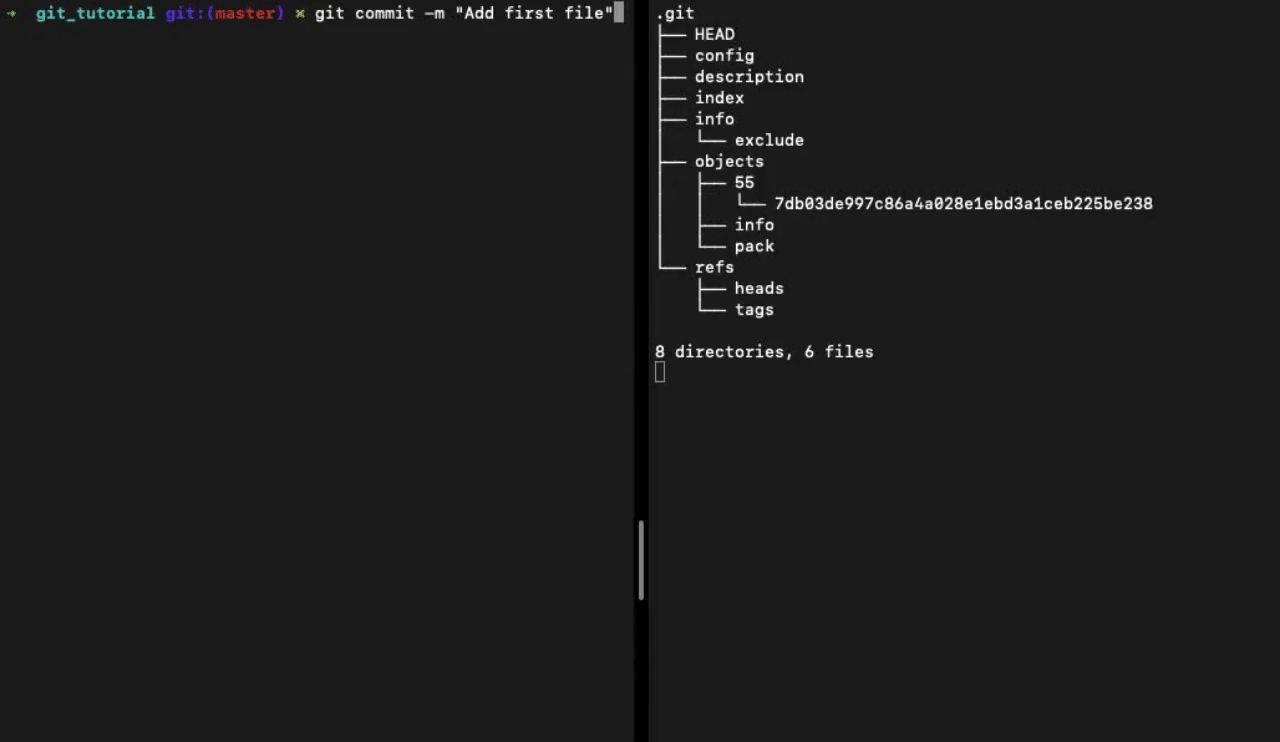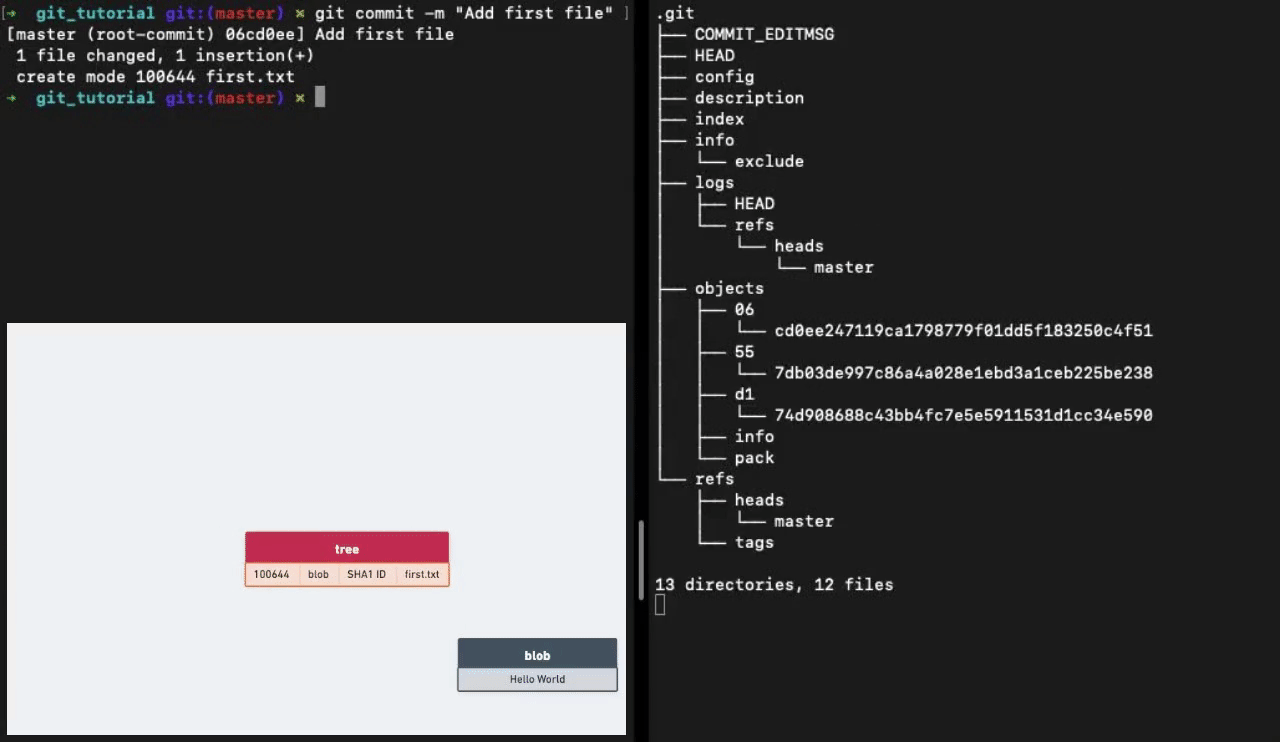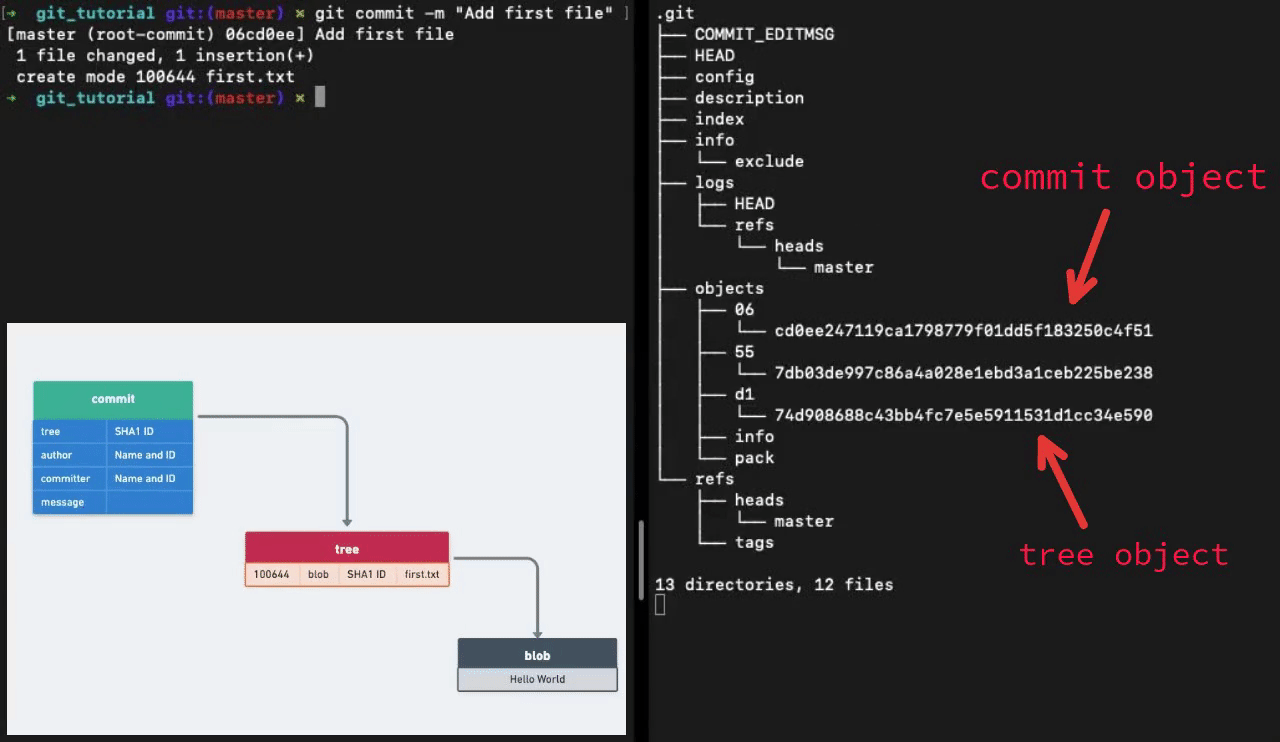
Git stores all the content as a directed acyclic graph using these different types of objects. Here is what the data structure would look like at this point of time.
Branches
A branch in Git is simply a lightweight movable pointer to one of the commit objects. Because of this reason, creating new branches in Git is “cheap”.
Every time you commit, the branch pointer moves forward automatically.
How does Git know what branch you’re currently on? It keeps a special pointer called HEAD. HEAD is nothing but a special pointer which points towards a branch. The branch that you are currently working on.
When we run the command git checkout -b <NAME> Git creates a new file in the refs/heads directory with the branch name. The file contains the pointer to the latest commit.
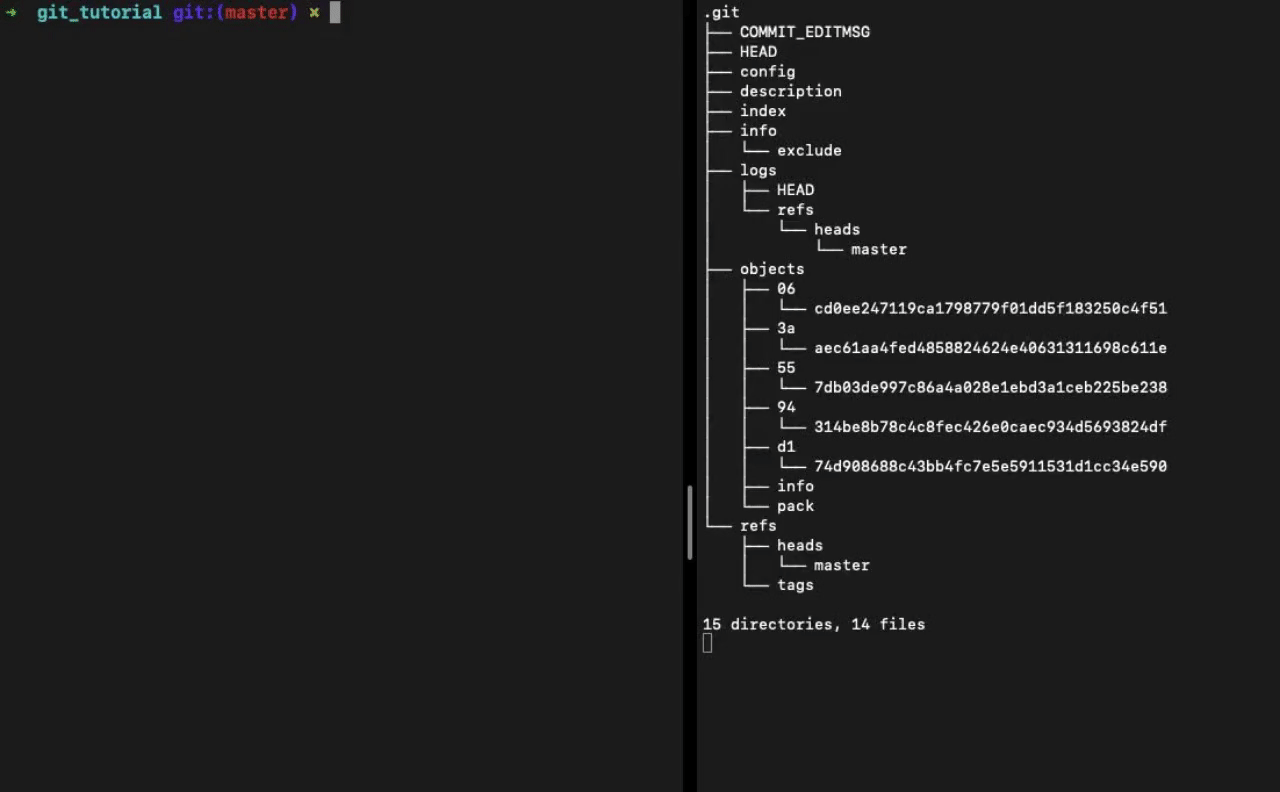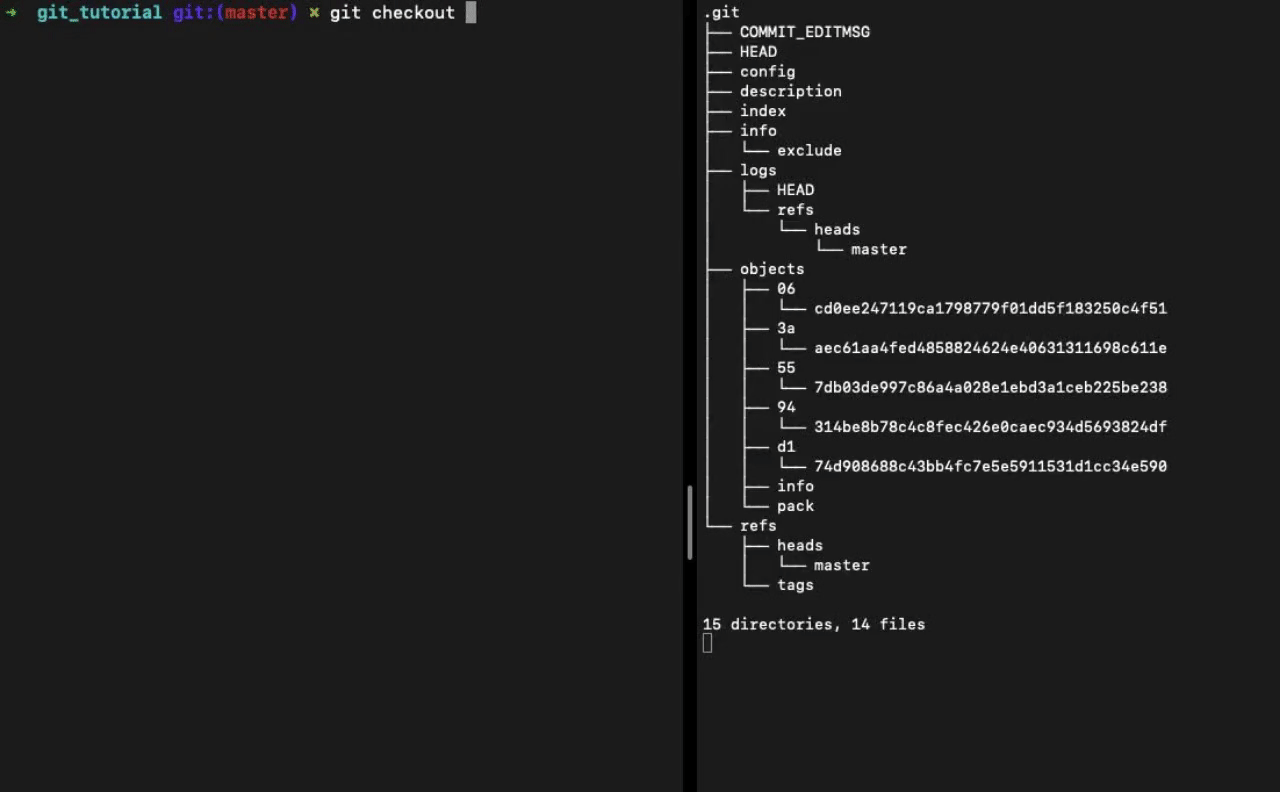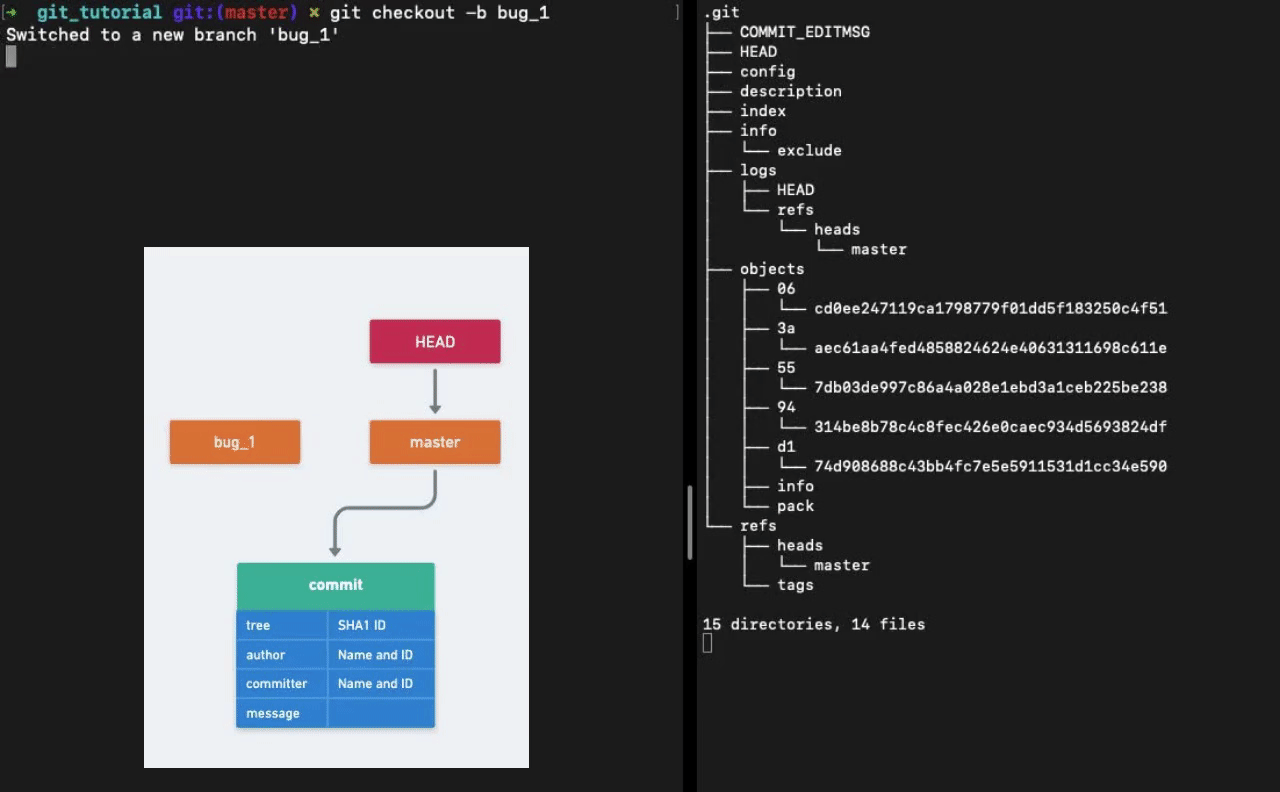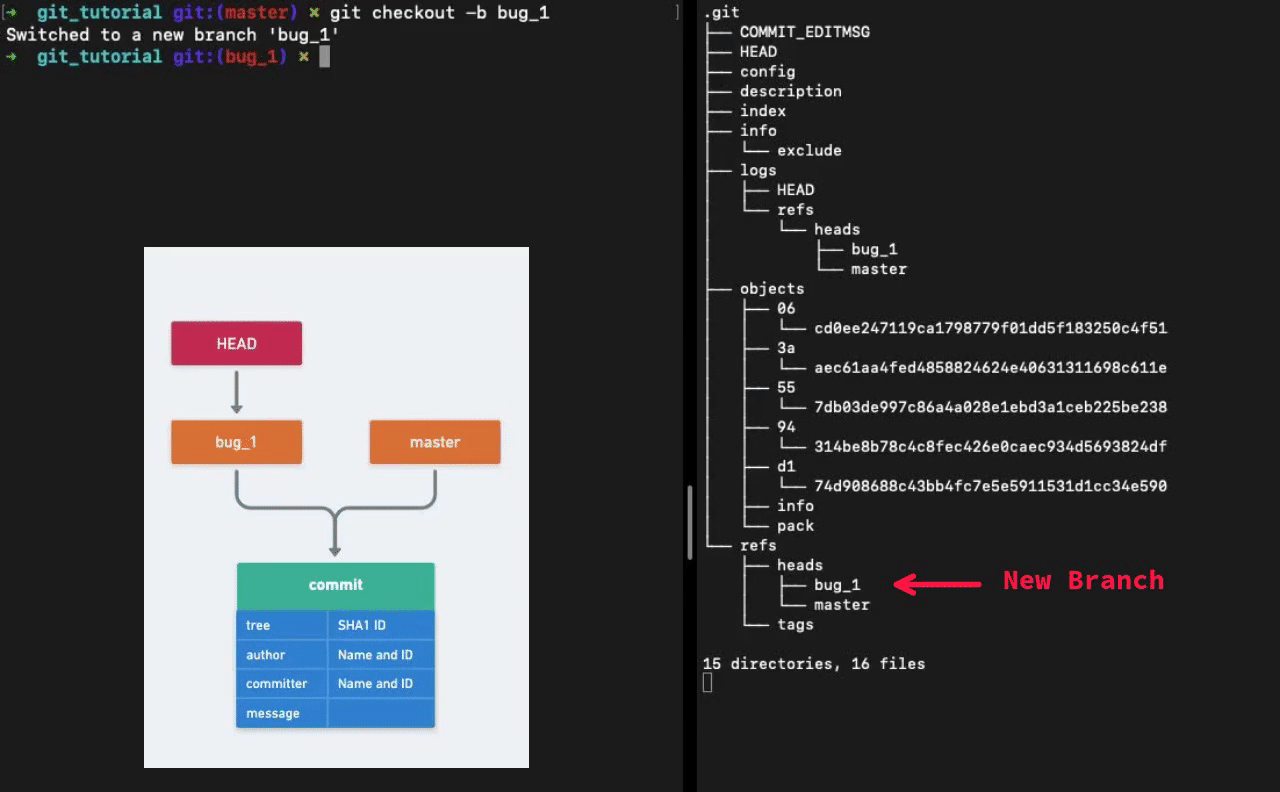
In conclusion, Git commands are an abstraction over the data storage. Hashes, file based key-value storage and tree data structure, these are the key things behind Git.
I am writing a book: Git Complete: The definitive, step-by-step guide to Git and Github as I have seen a lot of my friends, colleagues and students constantly make mistakes while using Git. So get your pre-order in and avail 50% discount. 😇
Feel free to reach out to me on Twitter.
Let me know what other architectural deep dives would you be interested in. Comment below. 👇